Oral antibiotics are one of the mainstays in the treatment of moderate to severe acne. I consider oral antibiotics for the treatment of acne when the acne lesions are deeper in the skin forming cysts or deep seated pustules, in which case topical treatments would be ineffective. The -cyline class of antibiotics is the most commonly used in the treatment of acne as they have great anti-inflammatory properties as well as a good side effect profile, especially with long term use. Doxycycline is my preferred -cycline as it is very efficacious, has minimal drug interactions, and a very low amount of long term side effects. I generally prescribe doxycycline 100mg twice a day for at least a 3 month course. At the end of three months, I reassess whether the patient needs to continue with doxycycline or it can be reduced to once a day dosing or discontinued completely. Doxycycline must be taken with food or it causes gastrointestinal upset. I recommend that patients eat a good breakfast and dinner before taking it. Also, it is important to take it with a big glass of water and remain upright for one hour after swallowing the pill to avoid esophagitis. Sun protection is mandatory with doxycycline as it is a very photosensitive drug and can cause severe sunburns. Minocycline is the most potent of the -cyclines but it also is burdened by a higher side effect profile if used for over a year continuously such as: staining of the permanent teeth, vertigo (dizziness), autoimmune hepatitis (liver damage), pigmentation deposits in the skin and oral mucosa, as well as a myriad other side effects. Other classes of antibiotics can be used such as erythromycin, clindamycin, keflex, amoxicillin and bactrim. 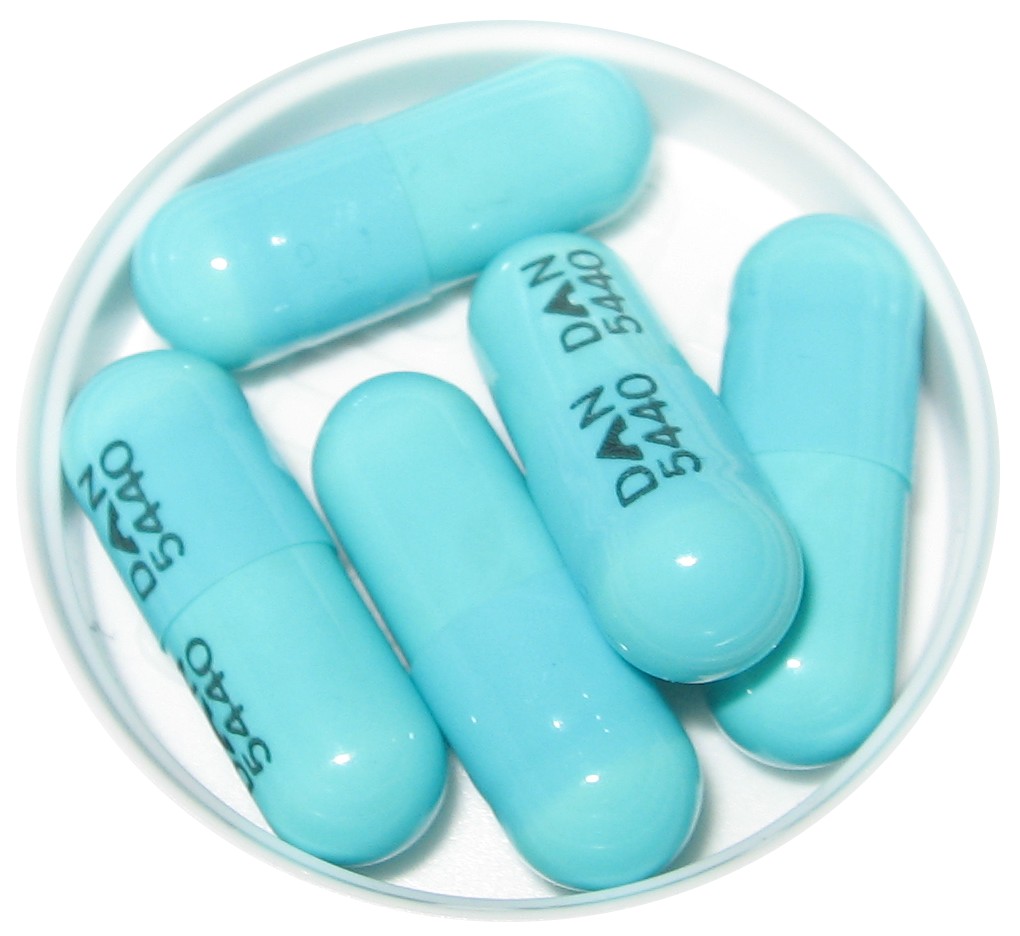
August 25, 2010